Digital Blueprints: A Review on Computer-Aided Design
- Madelyn Lee
- Aug 21, 2023
- 4 min read
As technology continues to expand and become more advanced, so has its manufacturing process. While you may remember the traditional handwritten blueprints for product manufacturing and architecture, it has been outgrown. With new technology becoming more intricate and complex, people around the world have turned to computer-aided design to model their desired creations.

Computer-aided design, commonly known as CAD, is a part of the manufacturing process that uses computer systems to digitally create, modify, analyze, and optimize 2D and 3D designs of products. It is essentially a representation of a component or whole real-world model and design on a computer screen. CAD is often used in a collaborative manner and is often complete with accurate scaling, precision, and physical properties to ensure that the CAD model is an exact digital copy of the real one.

There are many limitations with traditional manual designing. With the invention of computer-aided design, many of these issues have been resolved.
Computer-aided design software allows developers to easily modify their models by altering constraints and parameters. For example, if you change a parameter like the diameter of a circle, CAD software can automatically update the entire model to reflect this change, provided that the appropriate constraints are set. In comparison, a manual design would require the developer to start the design over and over again for each change, taking up mountainous amounts of time. CAD allows engineers to significantly shorten this time, increasing the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
With manual design, visibility and coherence may be a common concern, especially with more complex designs. This is because manual designs only have a limited amount of perspectives to view the model from. This makes the model more difficult to visualize and parts of the model may seem a little confusing. With computer-aided design, you can view the model from any angle possible in complete detail. You can easily zoom to view smaller components and rotate the model freely. This makes the model of the product simple to visualize.
Assembly using computer-aided design (CAD) is streamlined and efficient. CAD software allows designers to build complex models by assembling individual components rather than creating the entire model in one step. For example, if someone were designing a chair, they could split up the chair model into various components: chair seat, chair leg, chair back. Each component is designed in separate files and then brought together in an assembly file. This approach not only simplifies the design process but also enhances collaboration, enabling multiple team members to work on different parts of the model simultaneously and speed up the overall development.
One action that manual design can never accomplish is animation. Many CAD software packages include animation features that allow designers to simulate how a model will operate. This capability has transformed the manufacturing process by providing a preview of the model in action, revealing potential issues and optimizing performance before production begins.
The first ever true CAD software was a software called Sketchpad. It was developed in the 1960s by Ivan Sutherland at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Lincoln Laboratory. Sketchpad was a CAD software that allowed developers to sketch their designs on a computer monitor with precise lines and angles. It used a light stylist pen to interact with the computer monitor, allowing lines to appear on an empty digital canvas. As manufacturing and technology advanced, better software was created to improve efficiency and detail.
Where is CAD used in the world? Computer-aided design possesses applications across a variety of disciplines because of its wide range of abilities and level of intricacy. Some common applications include 3D printing, manufacturing, interior design, dentistry.
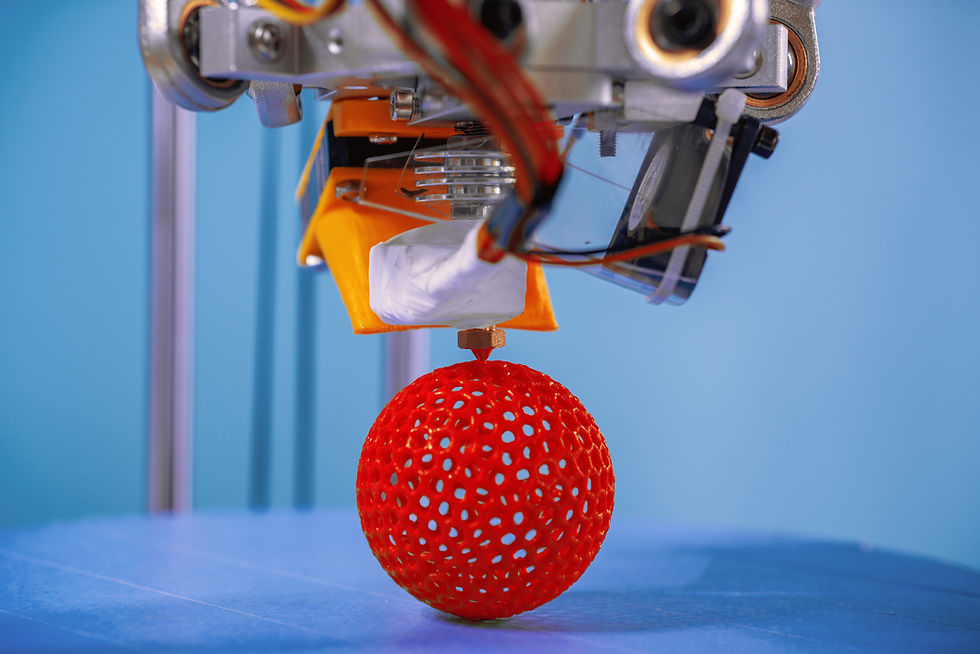
3D printing relies on CAD files to create physical objects. Once a model is designed in CAD software, the file is transferred to slicing software. This software “slices” the model into ultra-thin 2D layers, which guide the 3D printer in constructing the object layer by layer. Since 3D printers interpret only 2D instructions, they sequentially print each sliced layer to build up the final 3D object.

In manufacturing, CAD (computer-aided design) serves as the initial step for creating detailed models before transitioning to CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) software. Once a design is finalized in CAD, the model file is imported into CAM software, where it is prepared for production. In CAM, parameters for tools and cutting processes are configured to ensure precise machining. The final file is then sent to a CNC (computer numerical control) machine or similar equipment, which follows the file's instructions to cut and shape materials with high accuracy.

Interior design relies on CAD software to bring room layouts to life. These tools enable designers to experiment with different arrangements and assess the structural integrity of their designs. Whether using 2D or 3D CAD models, both designers and clients benefit from a clearer visualization of the final outcome, making it easier to refine and perfect the design before implementation.
Computer-aided design is an essential innovation in the fields of engineering and design because of its vast applications. It not only greatly improves detail and minimizes time, but it also allows the developers to simulate and test their designs within a computer screen. I hope you learned something new! Keep a lookout for the next post!
References
BasuMallick, C. (2022 Sep. 27). What is CAD (Computer Aided Design)? Definition, Types, and Applications. Spiceworks. Retrieved August 19, 2023, from https://www.spiceworks.com/tech/devops/articles/what-is-cad/
Goodwin University. (2022 Nov. 28). What is Computer-Aided Design (CAD)?. Goodwin University. Retrieved August 19, 2023, from https://www.goodwin.edu/enews/computer-aided-design-definition/
Ye, R. (2023 June 8). What is Computer-Aided Design: Definition, Types, Applications & Advantages. 3ERP. Retrieved August 19, 2023, from https://www.3erp.com/blog/computer-aided-design/
Comments