Layer by Layer: A Review on 3D Printing
- Madelyn Lee
- Jul 24, 2023
- 5 min read
We all know the incredible abilities of printers that can print any text or picture you send it, creating an exact replica of what you see on the computer screen. Unfortunately, they just print out the same two-dimensional image: just a flat paper version of the computer file. What if I told you it was possible to print out any three-dimensional object you wanted from plastic or resin? This type of printer is called a 3D printer.

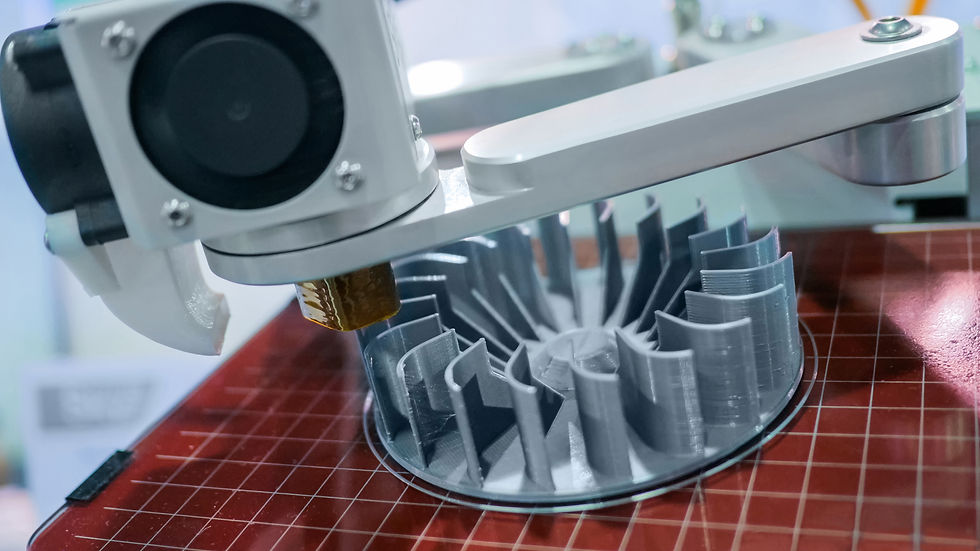
3D printing is a printing process that relies on computer-aided design to create three-dimensional objects layer by layer with materials such as plastics and resin. Instead of starting with a larger piece of material and removing material chunk by chunk like CNC machines, this type of method adds material onto existing material to create a product. This process is called additive manufacturing. There exists a variety of methods and machines for 3D printing. Different 3D printing machines have advantages in certain disciplines over others and vice versa. Three main types include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, Stereolithography (SLA) printers, and Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) printers.

Fused Deposition Modeling, or FDM, is most likely the method you would first think of when hearing the term 3D printing. It is the most commonly and widely used form of printing, especially on the consumer level. This would be the type of printer you would find in most households. FDM printers use thermoplastic filaments to create objects layer by layer. Essentially, a spool of plastic filament is unwound and inserted into a chamber called an extruder. This is where the plastic is melted. The melted plastic is then pushed through the nozzle, which is programmed to move in horizontal and vertical directions in order to form the target object as the plastic hardens.

Stereolithography, or SLA, is a 3D printing technique that uses laser or light sources to solidify photosensitive liquid resin into plastic. The solidification process is called curing. These resin 3D printers are able to print thinner layers than the FDM printers because the curing process is done point by point. This method offers models to have higher levels of detail and intricacy, making it suitable for disciplines such as dentistry and jewelers. SLA is also a relatively fast printing method, crafting products within hours.
Powder Bed Fusion, or PBF, is actually a whole collection of powder-based printing methods that use lasers to fuse powder particles together. The most common PBF methods include Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). With PBF printing, a powerful laser is aimed at a bed of powdered material and its heat melts and fuses certain particles together. These methods of printing often are used to 3D print metal and plastic materials.
There are a variety of printing materials that can be used in 3D printing. The most common materials include Polylactic Acid (PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), and Nylon. Polylactic Acid is the most common material in 3D printing because it is very versatile. It is made from biodegradable plastic that is formed from renewable sources, making 3D printing a viable eco-friendly method in comparison to many other manufacturing methods. PLA has a low melting point, is light in weight, but is also very durable. These qualities make it a perfect material for manufacturing use as well as consumer use. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a thermoplastic that is also fairly common. Also used in the popular bricks called LEGOs, the material is durable, flexible, lightweight, and cheap, making it suitable for products that require strength and ductility. ABS actually possesses better impact resistance and shock absorption than most polymers as well. Nylon is a plastic that is very durable and resistant to many effects. It possesses one of the highest melting points from all these materials, making it very heat resistant. Because of its exceptionally strong nature, nylon is relatively resistant to abrasion which is why it is often used in many industrial items. All these materials can be used in both filament printing and resin printing.

So how does the process of 3D printing work? 3D printing can be split into three distinct steps: CAD, Slicing, Printing. All of these steps allow the printer to be able to understand complex computer files and figure out where it needs to print to create a model.
CAD, also known as Computer-Aided Design, is a 3D modeling software. Through these types of software, people are able to create basically whatever they want. CAD allows the user to be able to design their models with intricate precision and detail, unlike traditional manufacturing methods. Once the 3D model is created in the CAD software, the file is sent to a slicing software.

Slicing software does exactly as you would imagine. It takes the 3D model from the CAD and slices it into many thin layers. Because the 3D printers cannot actually conceptualize the concept of a three dimensional model, the model must be sliced into 2D layers. Like a normal 2D printer, the slicing software then informs the 3D printer how to move in order to create each 2D layer. Each layer is basically a cross-section of the 3D model. If for example you were to print a cone shape, the bottom layer of the cone would be a circle and the top layer would just be a point. Slicing software will also tell the 3D printer where to add “fills.” Fills are thin structural components in the interior of a 3D printed model that help stabilize its shape.

Finally, the printing process begins. Each cross-section slice or layer is printed on top of one another. The nozzle moves up, down, back, and forth while exuding the plastic material. Thousands of 2D printed layers accumulate to make the 3D model from the CAD design.
3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry with its ability to recreate almost any three-dimensional object, lending it applications across a multitude of disciplines. By allowing people to bring complex and customized designs to life, 3D printing will likely become a main manufacturing method in the future. I hope you learned something new! Keep a lookout for the next post!
References
Cariki. (2023 Apr. 22). What are the advantages and disadvantages of nylon. Cariki. Retrieved July 18, 2023, from https://cariki.co.uk/blogs/the-green-road/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-nylon
Daley, S. & Powers, J. (2022 Jul. 28). How Does 3D Printing Work?. Built In. Retrieved July 18, 2023, from https://builtin.com/3d-printing
Dassault Systemes. (2022 Mar. 3). 3D Printing. Dassault Systemes. Retrieved July 18, 2023, from https://www.3ds.com/make/guide/process/3d-printing
Turney, D. (2023 May 19). Metal, concrete, and wood are the next frontiers in 3D-printing materials. Autodesk. Retrieved July 18, 2023, from https://www.autodesk.com/design-make/articles/what-materials-are-used-in-3d-printing
Woodford, C. (2023 Feb. 5). 3D printers. Explainthatstuff. Retrieved July 18, 2023, from https://www.explainthatstuff.com/how-3d-printers-work.html
Comentarios